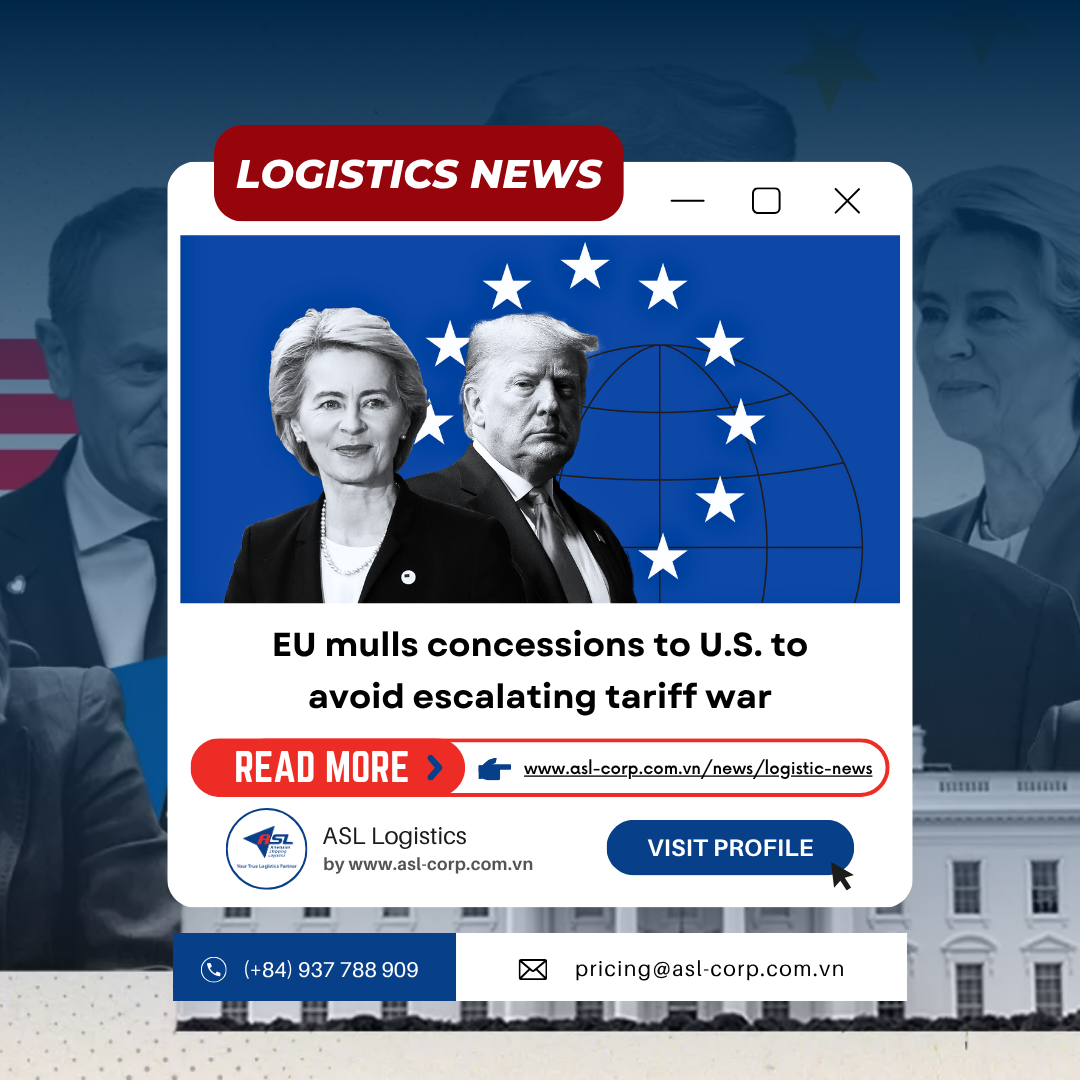
U.S. President Donald Trump has just threatened to immediately impose a 100% tariff on goods imported from Canada if the country proceeds with a preliminary trade agreement with China. The move has raised concerns over potential disruptions to North America’s automotive and energy supply chains, despite commitments under the USMCA.
Logistic News
BRIDGE COLLAPSE ON THE EAST COAST OF THE US: A STRONG BLOW TO THE GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAIN AND ACCOMPANYING ECONOMIC DAMAGE
04 April 2024
The collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge at Baltimore Port in Maryland, USA is considered the worst bridge collapse disaster since 2007 and this is also the first bridge crash due to a collision with a cargo ship in the past 40 years. This serious accident had a widespread impact on the entire economy of the United States when the main waterway transporting important goods caused indefinite disruption to the ships' flow and strained the supply chain on the East Coast of the United States.
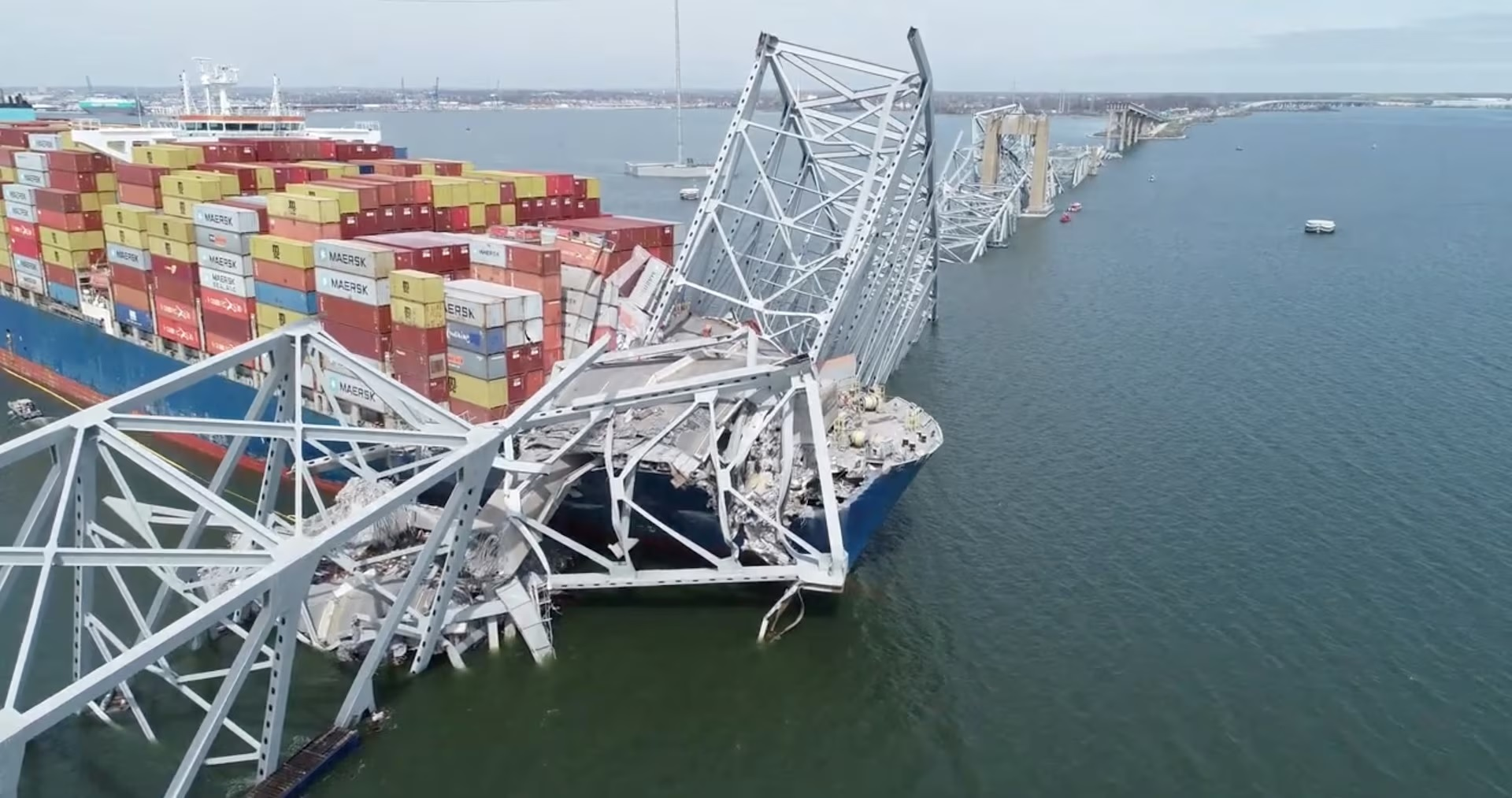

The scene of the Francis Scott Bridge in Baltimore, Maryland after being hit by the Singapore container ship named Dali
Early on Tuesday morning (March 26), a large container ship chartered by Maersk and owned by Singaporean company Grace Ocean on its journey to Sri Lanka crashed into the bridge, causing the bridge structure to break and collapse instantly, leading to many cars and at least 20 people are said to have fallen into the river.
Media announcement after the collision
Maryland Governor Wes Moore commented that this is not just about Maryland’s economy, this is about the entire national economy. The river route is congested because the bridge collapsed, which was the first point leading into Baltimore Port, one of the busiest and most frequently operated ports in the United States.
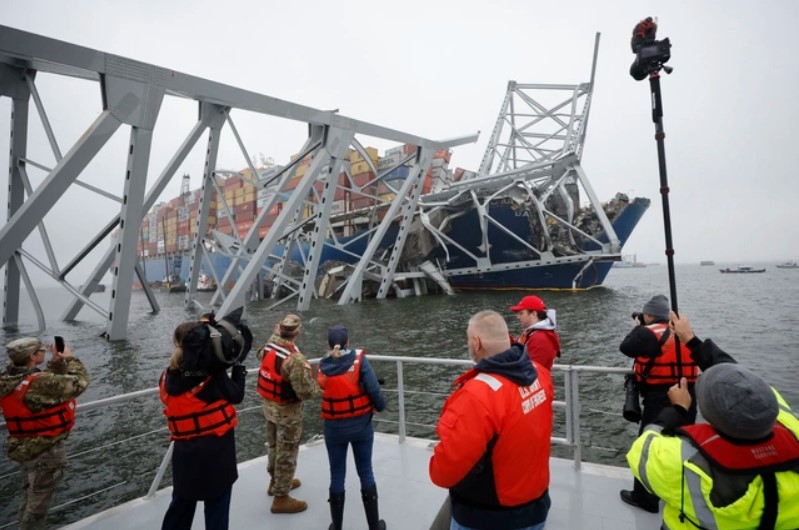

Meanwhile, Minister of the US Ministry of Transport, Pete Buttigieg said that getting this seaport back into operation soon is not only important for the people and workers in Baltimore but also for the country's supply chains. He said, the work of cleaning and clearing this river route began on March 30 and is being carried out urgently but it is unknown when it will be completed. The time frame for rebuilding the bridge also cannot be estimated. Federal officials and local officials are concerned that the operation to clear the scene and rebuild the collapsed bridge will be unexpected and complicated.
"We will bypass Baltimore on all of our routes for the foreseeable future until the situation is deemed safe for transit through the region", Maersk stated in their latest announcement. They said they would unload cargo bound for Baltimore at other nearby ports, but it also meant delayed delivery.

Serious consequences the global supply chain must bear
According to Maryland statistics, in 2023, the Port of Baltimore received and coordinated about 1.1 million containers of goods, making it the 9th busiest port in the country in terms of trade volume. In 2023, with the handling of more than 850,000 cars and light-duty vehicles, the Baltimore Port ranked first in the United States for the 13th consecutive year in this field. The suspension of goods trade to overcome the consequences of the accident will cause car manufacturers such as BMW and Volkswagen to be the most affected at this time due to their heavy dependence on ports. Consumer customers looking to buy new cars also had to delay for a while due to supply shortages. Not only retail corporations such as Under Armour, Home Depot, and IKEA are affected by the lack of circulation, but farmers and restaurant owners can also feel some short-term impacts.
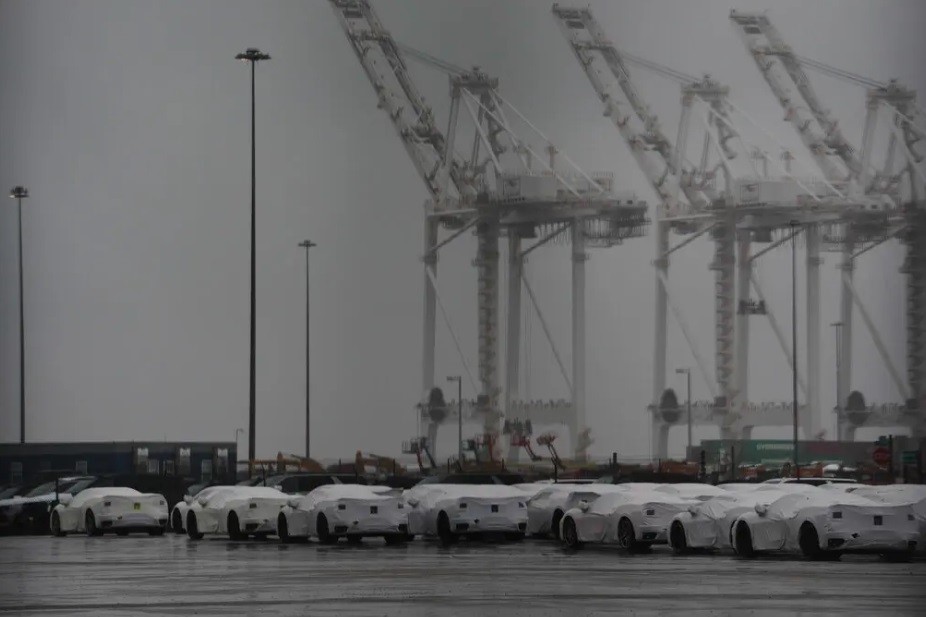

The Baltimore Port is smaller than the largest container terminals in the United States, but it is a major component of the vehicle supply chain.
“The catastrophic collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge will put pressure on other modes of transportation and port alternatives,” said Jason Eversole, CEO at FourKites, a supply chain consulting firm". Some goods that would have gone through Baltimore likely ended up in Charleston, Norfolk, or Savannah.
That will increase demand for road and rail transport services and make getting goods to their destinations more complicated and expensive. “Even if they clear the debris from the water, traffic in the area will be affected as truck drivers become reluctant to haul goods in and out of the area if prices do not increase,” Mr. Eversole said.
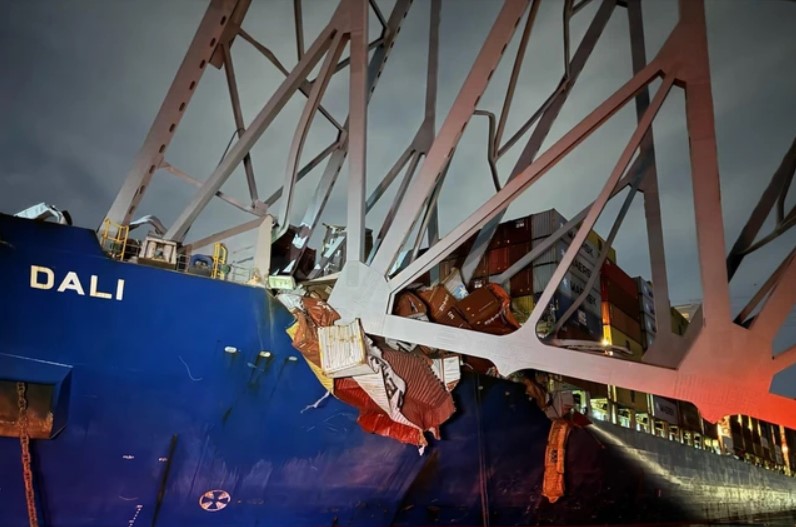

The bridge hit left losses to the economy due to the suspension of trade in goods
Dr. Richard Clinch, an economic and financial analyst as well as executive director of the Jacob France Institute at the University of Baltimore, said the Baltimore Port matters. He said the long-term impact of the bridge collapse depends on how long it takes to repair and rebuild the bridge. With little clarity on when the Port of Baltimore will reopen, insurers and analysts are now assessing losses related to property, cargo, maritime security, liability, trade credit, and business interruption.
Economic compensation for the bridge collapse could be the largest in maritime history
Maryland officials estimate that the state's economy loses up to $15 million every day due to the bridge collapse. Additionally, 15,000 direct port jobs and another 140,000 indirect jobs dependent on the Baltimore Port are affected. According to forecasts by maritime risk management company, Windward, cargo ships to Baltimore port will have to be delayed for at least 24 days.
Particularly large losses are likely to fall on insurance companies. Depending on the duration of the blockage and the nature of the business interruption coverage for the Port of Baltimore, insured losses could amount to from 2 billion USD to 4 billion USD. He said this figure would exceed the record insured loss of the Costa Concordia luxury cruise ship disaster in 2012. Senior director in charge of analytics at insurance rating agency AM Best, Mr. Mathilde Jakobsen, also said compensation payments could extend to billions of dollars.
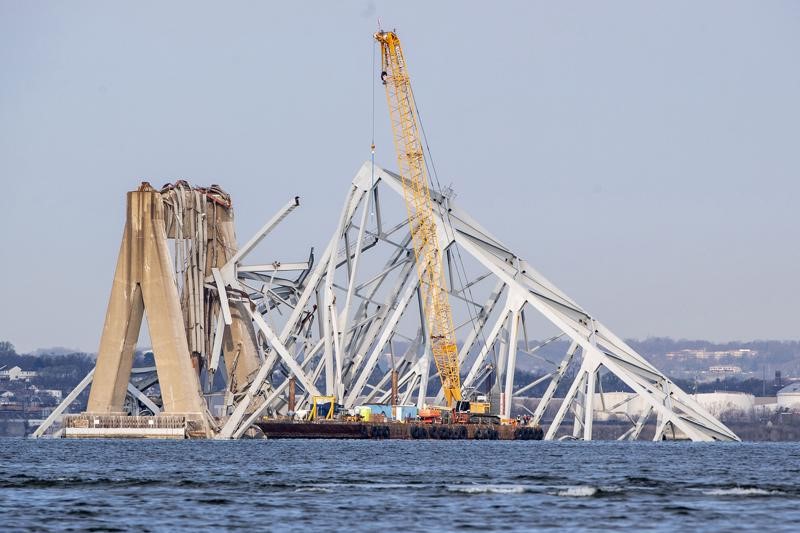

The bridge breakdown will impose a minimum 24-day delay for freight ships bound for the Port of Baltimore.
Currently, ships that should be entering Baltimore are anchored outside the port and waiting to be redirected to other ports on the East Coast. Ports in Philadelphia, Wilmington, Newark, Norfolk, Charleston, Jacksonville... may have to receive an increased amount of goods entering.
According to the Associated Press, the cost of rebuilding the Francis Scott Key Bridge will range from $400 million to $1 billion, and the time to complete the project will take from 18 months to several years. Meanwhile, closing the Baltimore port for a month could cost the state of Maryland a total of $28 million. US President Joe Biden has announced that the federal government will pay for rebuilding the bridge, but experts say there is no guarantee of this.
Hopes for a more positive future
According to forecasts by maritime risk management company Windward, although cargo ships arriving at Baltimore will have to be delayed for at least 24 days, this disruption to goods circulation will hold for a short term and is controllable as Baltimore only accounts for about 4% of trade volume on the US East Coast.
Supply chain experts say U.S. port infrastructure is better now than it was in 2021-2022 when ports were severely understaffed while dealing with a massive backlog of ships and goods stagnation due to the impact of COVID-19. Congestion during the pandemic has caused cargo to surge, but experts say the bridge collapse in Baltimore will not have a similar widespread impact.
Chief economist Ryan Sweet of Oxford Economics research firm said: "The bridge collapse will have a greater economic impact on local Baltimore than on a national scale. We do not expect that disruptions to transportation or trade due to this incident will be evident in US economic growth. The impact on inflation is also minimal and under control."
Ms. Emily Stausolll, an analyst at Xeneta, added: Freight companies will have solutions to overcome the problem such as importing additional containers to neighboring ports like New York/New Jersey if Baltimore is inaccessible, so any impact on ocean freight rates will likely be limited.
Conclusion: The bridge collapse on the East Coast of the United States caused a series of serious economic losses and was a reminder of the importance of ensuring safety and maintaining transportation infrastructure. The most important thing is to make preparations to ensure the stability of the global supply chain against disasters that can happen at any time.
Source: The Epoch Times

Head Office
ASL Hồ Chí Minh
Số 31/34A Ung Văn Khiêm, Phường Thạnh Mỹ Tây, TP. Hồ Chí Minh, Việt Nam
 Công Ty Cổ Phần Giao Nhận Vận Tải Mỹ Á
Công Ty Cổ Phần Giao Nhận Vận Tải Mỹ Á
 (+84)28 3512 9759
(+84)28 3512 9759
 (+84)28 3512 9758
(+84)28 3512 9758
 pricing@asl-corp.com.vn
pricing@asl-corp.com.vn
 mdirector@asl-corp.com.vn
mdirector@asl-corp.com.vn
 www.asl-corp.com.vn
www.asl-corp.com.vn
LOGISTICS SERVICES













.png)
.png)

.png)